MSD European Ford Coil Pack
Ford Coil Pack
Features
- Designed to be used with late model Ford waste spark ignition systems
- 83:1 turns ratio and lower primary resistance produce high voltage output
- Secondary towers designed for snap on spark plug terminals
- Primary terminals require Ford style connector
- CARB E.O. Approved
| Coil Specs | |
| Turns ratio: | 83:1 |
| Primary resistance: | .53 OHMs |
| Secondary resistance: | 13.7K OHMs |
| Inductance: | 3.9mH |
| Maximum voltage: | 40,000 Volts |
| Peak current: | N/A |
| Spark duration: | N/A |
| Weight: | 1140g |

European Ford Coil Pack Table
| RB Key | Type | Model Range | Litres | kW | Year of manufacture | Engine no. |
| FOR 1807 | Courier 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 07/1997 - 08/1999 | JKKC | |
| FOR 1808 | Courier 1.4i 16V | 14 | 66 | 07/1997 - 08/1999 | FVKB | |
| FOR 1787 | Escort 1.8i 16V | 18 | 85 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | RKD | |
| FOR 1269 | Escort IV 1.1 | 86 | 11 | 40 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | GUC |
| FOR 1268 | Escort IV 1.1 Express | 86 | 11 | 40 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | GUC |
| FOR 1130 | Escort IV 1.3 | 86 | 13 | 44 - 46 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | JB... |
| FOR 3188 | Escort IV 1.3 Express | 86 | 13 | 44 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | JBB |
| FOR 3189 | Escort IV 1.3 Express | 86 | 13 | 46 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | JBA |
| FOR 1131 | Escort IV 1.3 Turnier | 86 | 13 | 44 - 46 | 08/1988 - 07/1990 | JB... |
| FOR 3079 | Escort IV 1.4 | 86 | 14 | 51 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | FUAA |
| FOR 946 | Escort IV 1.4 | 86 | 14 | 54 | 02/1987 - 07/1990 | FUC |
| FOR 480 | Escort IV 1.4 | 86 | 14 | 55 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | FUA |
| FOR 590 | Escort IV 1.4 Cabrio | 86 | 14 | 51 - 55 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | FUA... |
| FOR 947 | Escort IV 1.4 Cabrio | 86 | 14 | 54 | 02/1987 - 07/1990 | FUC |
| FOR 1133 | Escort IV 1.4 Express | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | FUC |
| FOR 589 | Escort IV 1.4 Turnier | 86 | 14 | 51 - 55 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | FUA... |
| FOR 948 | Escort IV 1.4 Turnier | 86 | 14 | 54 | 02/1987 - 07/1990 | FUC |
| FOR 963 | Escort IV 1.4i | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1987 - 07/1990 | F6B |
| FOR 3085 | Escort IV 1.4i | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1987 - 07/1990 | F6D |
| FOR 980 | Escort IV 1.4i Cabrio | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1987 - 07/1990 | F6... |
| FOR 3197 | Escort IV 1.4i Express | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | F6... |
| FOR 981 | Escort IV 1.4i Turnier | 86 | 14 | 54 | 01/1987 - 07/1990 | F6... |
| FOR 1270 | Escort IV 1.6 | 86 | 16 | 58 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LP2 |
| FOR 3095 | Escort IV 1.6 | 86 | 16 | 65 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LUG |
| FOR 481 | Escort IV 1.6 | 86 | 16 | 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LUC |
| FOR 3074 | Escort IV 1.6 Cabrio | 86 | 16 | 58 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LP2 |
| FOR 611 | Escort IV 1.6 Cabrio | 86 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LU... |
| FOR 654 | Escort IV 1.6 Express | 86 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LU... |
| FOR 477 | Escort IV 1.6 RS Turnier | 86 | 16 | 97 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LNB |
| FOR 1271 | Escort IV 1.6 Turnier | 86 | 16 | 58 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LP2 |
| FOR 591 | Escort IV 1.6 Turnier | 86 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LU... |
| FOR 609 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i | 86 | 16 | 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | L4B |
| FOR 608 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i | 86 | 16 | 75 | 08/1989 - 07/1990 | LJB |
| FOR 3076 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i | 86 | 16 | 77 | 01/1986 - 08/1989 | LR2 |
| FOR 476 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i | 86 | 16 | 77 | 01/1986 - 08/1989 | LRB |
| FOR 594 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i | 86 | 16 | 79 | 08/1989 - 07/1990 | LJA |
| FOR 3075 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i C | 86 | 16 | 75 | 08/1989 - 07/1990 | LJB |
| FOR 3078 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i C | 86 | 16 | 77 | 01/1986 - 08/1989 | LR2 |
| FOR 3077 | Escort IV 1.6 XR3i C | 86 | 16 | 77 | 01/1986 - 08/1989 | LRB |
| FOR 407 | Escort IV 1.6i | 86 | 16 | 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | L4B |
| FOR 593 | Escort IV 1.6i Cabrio | 86 | 16 | 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | L4B |
| FOR 607 | Escort IV 1.6i Turnier | 86 | 16 | 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | L4B |
| FOR 1788 | Escort SW 1.8i 16V | 18 | 85 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | RKD | |
| FOR 2665 | Escort Sedan 1.8i 16 | 18 | 85 | 09/1996 - 02/2000 | RKD | |
| FOR 1310 | Escort V/VI 1.1 | 91 | 11 | 40 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | GUF |
| FOR 1313 | Escort V/VI 1.4 | 91 | 14 | 54 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | FUH |
| FOR 1384 | Escort V/VI 1.4 Turnier | 91 | 14 | 54 | 08/1990 - 09/1992 | FUH |
| FOR 1314 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6F |
| FOR 3086 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6G |
| FOR 3301 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 52 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | F6F |
| FOR 3302 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 52 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | F6G |
| FOR 3299 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 54 - 55 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | F4B |
| FOR 1809 | Escort V/VI 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 54 - 55 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | F4B |
| FOR 1474 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Cabrio | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6F |
| FOR 3098 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Cabrio | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6G |
| FOR 3300 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Cabrio | 91 | 14 | 54 - 55 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | F4B |
| FOR 1330 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Express | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6F |
| FOR 3099 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Express | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6G |
| FOR 1382 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Turnier | 91 | 14 | 52 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | F6F |
| FOR 1550 | Escort V/VI 1.4i Turnier | 91 | 14 | 54 - 55 | 02/1994 - 12/1994 | F4B |
| FOR 3100 | Escort V/VI 1.6 Turnier | 91 | 16 | 66 | 08/1990 - 12/1994 | LUK |
| FOR 3182 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 65 | 09/1992 - 12/1994 | L1H |
| FOR 3304 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 65 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | L1H |
| FOR 1473 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 66 | 09/1992 - 12/1994 | L1E |
| FOR 3303 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 66 | 07/1993 - 12/1994 | L1E |
| FOR 3184 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 65 | 02/1993 - 12/1994 | L1H |
| FOR 1512 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 66 | 02/1993 - 12/1994 | L1E |
| FOR 3183 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 65 | 09/1992 - 12/1994 | L1H |
| FOR 1478 | Escort V/VI 1.6i 16V | 91 | 16 | 66 | 09/1992 - 12/1994 | L1E |
| FOR 1436 | Escort V/VI 1.8 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 02/1992 - 12/1994 | RDA |
| FOR 1437 | Escort V/VI 1.8 XR3i | 91 | 18 | 96 | 02/1992 - 12/1994 | RQB |
| FOR 1439 | Escort V/VI 1.8 XR3i | 91 | 18 | 96 | 02/1992 - 12/1994 | RQB |
| FOR 3309 | Escort V/VI 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 03/1992 - 12/1994 | RDA |
| FOR 1435 | Escort V/VI 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 03/1992 - 12/1994 | RDA |
| FOR 1438 | Escort V/VI 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 02/1992 - 12/1994 | RDA |
| FOR 1479 | Escort V/VI 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 03/1992 - 12/1994 | RDA |
| FOR 3097 | Escort V/VI 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 96 | 02/1992 - 12/1994 | RQB |
| FOR 3311 | Escort VII 1.3i | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J4B |
| FOR 1705 | Escort VII 1.3i | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J4B |
| FOR 3310 | Escort VII 1.3i | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J6A |
| FOR 1603 | Escort VII 1.3i | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J6A |
| FOR 1706 | Escort VII 1.3i Turnier | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J4B |
| FOR 1604 | Escort VII 1.3i Turnier | 95 | 13 | 44 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | J6A |
| FOR 3312 | Escort VII 1.4i | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 1605 | Escort VII 1.4i | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 1838 | Escort VII 1.4i Cabrio | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 1623 | Escort VII 1.4i Express | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 1626 | Escort VII 1.4i Express | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 1606 | Escort VII 1.4i Turnier | 95 | 14 | 54 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | F4B |
| FOR 3314 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 65 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1H |
| FOR 1710 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 65 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1H |
| FOR 3313 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1E |
| FOR 2963 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1E |
| FOR 3315 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1K |
| FOR 1709 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1K |
| FOR 1607 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1E |
| FOR 1612 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 65 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1H |
| FOR 2976 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1E |
| FOR 1707 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1K |
| FOR 1711 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 65 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1H |
| FOR 3185 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1E |
| FOR 1609 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1K |
| FOR 1708 | Escort VII 1.6i 16V | 95 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | L1K |
| FOR 3319 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 77 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | RDA |
| FOR 1611 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 77 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | RDA |
| FOR 3320 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 85 | 09/1995 - 09/2001 | RKC |
| FOR 1712 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 85 | 09/1995 - 09/2001 | RKC |
| FOR 1610 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 77 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | RDA |
| FOR 1713 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 85 | 09/1995 - 09/2001 | RKC |
| FOR 1616 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 77 | 01/1995 - 09/2001 | RDA |
| FOR 1714 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 85 | 09/1995 - 09/2001 | RKC |
| FOR 1617 | Escort VII 1.8i 16V | 95 | 18 | 96 | 01/1995 - 08/1995 | RQB |
| FOR 1953 | Fairlane | AU | 50 | 175 | 02/1999 - 06/2000 | Z |
| FOR 2132 | Fairlane | AU II | 50 | 175 | 07/2000 - 02/2003 | Z |
| FOR 1932 | Fairmont | AU | 50 | 175 | 09/1998 - 03/2000 | Z |
| FOR 2134 | Fairmont | AU II | 50 | 175 | 04/2000 - 09/2001 | Z |
| FOR 2817 | Fairmont | AU III | 50 | 175 | 10/2001 - 09/2002 | Z |
| FOR 1925 | Falcon | AU | 50 | 175 | 09/1998 - 03/2000 | Z |
| FOR 2109 | Falcon | AU II | 50 | 175 | 04/2000 - 03/2001 | Z |
| FOR 2826 | Falcon | AU III | 50 | 175 | 04/2001 - 09/2002 | Z |
| FOR 3658 | Falcon Utility | AU II | 50 | 175 | 04/2000 - 09/2001 | Z |
| FOR 3666 | Falcon Utility | AU III | 50 | 175 | 10/2001 - 09/2002 | Z |
| FOR 3660 | Falcon Utility XR8 | AU II | 50 | 185 | 04/2000 - 09/2001 | Z |
| FOR 1926 | Falcon XR8 | AU | 50 | 185 | 09/1998 - 02/2000 | Z |
| FOR 2128 | Falcon XR8 | AU II | 50 | 200 | 04/2000 - 03/2001 | Z |
| FOR 2825 | Falcon XR8 | AU III | 50 | 200 | 04/2001 - 09/2002 | Z |
| FOR 1070 | Fiesta 1.0 | 89 | 10 | 33 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | TLB |
| FOR 1743 | Fiesta 1.0i | 10 | 29 | 04/1996 - 08/1999 | C4A | |
| FOR 1048 | Fiesta 1.1 | 89 | 11 | 40 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | GU... |
| FOR 1049 | Fiesta 1.1i | 89 | 11 | 36 - 37 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | G6A |
| FOR 1703 | Fiesta 1.25i 16V | 96 | 12 | 55 | 11/1995 - 12/2002 | DH... |
| FOR 1454 | Fiesta 1.3 | 89 | 13 | 44 | 06/1991 - 12/1996 | JBC |
| FOR 1744 | Fiesta 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 04/1996 - 08/1999 | J4E | |
| FOR 1362 | Fiesta 1.3i | 89 | 13 | 43 - 44 | 06/1991 - 12/1996 | J6B |
| FOR 1700 | Fiesta 1.3i | 96 | 13 | 37 | 11/1995 - 12/2002 | JJ... |
| FOR 1701 | Fiesta 1.3i | 96 | 13 | 44 | 11/1995 - 12/2002 | J4... |
| FOR 1413 | Fiesta 1.3i Courier | 89 | 13 | 44 | 09/1991 - 08/1996 | J6B |
| FOR 1918 | Fiesta 1.3i Courier | 96 | 13 | 44 | 11/1995 - 12/2002 | J4... |
| FOR 1335 | Fiesta 1.4 | 89 | 14 | 54 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | FU... |
| FOR 1050 | Fiesta 1.4 | 89 | 14 | 55 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | FUF |
| FOR 2355 | Fiesta 1.4 i | 14 | 55 | 10/1998 - 02/2000 | ||
| FOR 2548 | Fiesta 1.4 i | 14 | 55 | 03/2000 - 12/2004 | ||
| FOR 3679 | Fiesta 1.4 i | 14 | 60 | 02/2004 - 12/2008 | ||
| FOR 1051 | Fiesta 1.4i | 89 | 14 | 52 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | F6E |
| FOR 1543 | Fiesta 1.4i | 89 | 14 | 54 - 55 | 01/1994 - 12/1996 | F4A |
| FOR 1745 | Fiesta 1.4i 16V | 14 | 66 | 04/1996 - 08/1999 | FHC | |
| FOR 1727 | Fiesta 1.4i 16V | 96 | 14 | 66 | 01/1996 - 12/2000 | FH... |
| FOR 1738 | Fiesta 1.4i Courier | 96 | 14 | 66 | 01/1996 - 12/2000 | FH... |
| FOR 1071 | Fiesta 1.6 | 89 | 16 | 66 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | LUH |
| FOR 1288 | Fiesta 1.6 Turbo | 89 | 16 | 96 - 98 | 07/1990 - 12/1996 | LHA |
| FOR 1053 | Fiesta 1.6 XR2i | 89 | 16 | 76 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | LJD |
| FOR 1052 | Fiesta 1.6 XR2i | 89 | 16 | 81 | 03/1989 - 12/1996 | LJC |
| FOR 2364 | Fiesta 1.6 i | 16 | 70 | 08/2000 - 12/2004 | ||
| FOR 3678 | Fiesta 1.6 i | 16 | 74 | 02/2004 - 12/2008 | ||
| FOR 1542 | Fiesta 1.6i 16V | 89 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 02/1994 - 12/1996 | L1G |
| FOR 1433 | Fiesta 1.8 XR2i 16V | 89 | 18 | 77 | 02/1992 - 12/1996 | RDA |
| FOR 1434 | Fiesta 1.8 XR2i 16V | 89 | 18 | 93 - 96 | 02/1992 - 12/1996 | RQC |
| FOR 1432 | Fiesta 1.8i 16V | 89 | 18 | 77 | 02/1992 - 12/1996 | RDB |
| FOR 1097 | Granada III 2.0i | 85 | 20 | 88 - 93 | 06/1989 - 01/1992 | N9... |
| FOR 2396 | Ikon 1.6 i | 16 | 70 | 02/2001 - | ||
| FOR 1785 | Ka 1.0i | 10 | 29 | 01/1997 - 07/1999 | C4B | |
| FOR 2511 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 36 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJD | |
| FOR 2512 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 36 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJF | |
| FOR 2513 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 36 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJG | |
| FOR 2514 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 36 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJH | |
| FOR 2515 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 36 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJL | |
| FOR 1756 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 37 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | JJB | |
| FOR 1755 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4D | |
| FOR 1898 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4K | |
| FOR 2516 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4M | |
| FOR 2517 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4N | |
| FOR 2518 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4P | |
| FOR 2519 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 09/1996 - 10/2002 | J4S | |
| FOR 1786 | Ka 1.3i | 13 | 44 | 01/1997 - 08/1999 | J4G | |
| FOR 1950 | LTD | AU | 50 | 185 | 05/1999 - 05/2000 | Z |
| FOR 2130 | LTD | AU II | 50 | 185 | 06/2000 - 06/2003 | Z |
| FOR 1733 | Mondeo I 1.6i | 93 | 16 | 65 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | L1... |
| FOR 1481 | Mondeo I 1.6i | 93 | 16 | 66 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | L1... |
| FOR 1734 | Mondeo I 1.6i Turnier | 93 | 16 | 65 | 04/1993 - 07/1996 | L1J |
| FOR 1487 | Mondeo I 1.6i Turnier | 93 | 16 | 66 | 04/1993 - 07/1996 | L1F |
| FOR 1735 | Mondeo I 1.8i | 93 | 18 | 82 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | RKB |
| FOR 3391 | Mondeo I 1.8i | 93 | 18 | 82 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | RKB |
| FOR 3389 | Mondeo I 1.8i | 93 | 18 | 85 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | RKA |
| FOR 1482 | Mondeo I 1.8i | 93 | 18 | 85 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | RKA |
| FOR 3390 | Mondeo I 1.8i 4x4 | 93 | 18 | 85 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | RKA |
| FOR 1736 | Mondeo I 1.8i Turnier | 93 | 18 | 82 | 04/1993 - 07/1996 | RKB |
| FOR 1489 | Mondeo I 1.8i Turnier | 93 | 18 | 85 | 04/1993 - 07/1996 | RKA |
| FOR 3392 | Mondeo I 2.0i | 93 | 20 | 97 - 100 | 07/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 1483 | Mondeo I 2.0i | 93 | 20 | 100 | 01/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 3393 | Mondeo I 2.0i 4x4 | 93 | 20 | 97 - 100 | 07/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 1685 | Mondeo I 2.0i 4x4 | 93 | 20 | 97 - 100 | 07/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 1490 | Mondeo I 2.0i Turnier | 93 | 20 | 100 | 04/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 1686 | Mondeo I 2.0i Turnier | 93 | 20 | 97 - 100 | 07/1993 - 07/1996 | NGA |
| FOR 1757 | Mondeo II 1.6i | 97 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 08/1996 - 08/1998 | L1J |
| FOR 3395 | Mondeo II 1.6i | 97 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 08/1996 - 08/1998 | L1J |
| FOR 1758 | Mondeo II 1.6i Turnier | 97 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 08/1996 - 08/1998 | L1J |
| FOR 3398 | Mondeo II 1.8i | 97 | 18 | 85 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | RK... |
| FOR 1759 | Mondeo II 1.8i | 97 | 18 | 85 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | RKB |
| FOR 1760 | Mondeo II 1.8i Turnier | 97 | 18 | 85 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | RKB |
| FOR 2560 | Mondeo II 1.8i Turnier | 97 | 18 | 85 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | RKK |
| FOR 3399 | Mondeo II 2.0i | 97 | 20 | 96 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | NG... |
| FOR 1761 | Mondeo II 2.0i | 97 | 20 | 96 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | NGA |
| FOR 2561 | Mondeo II 2.0i | 97 | 20 | 96 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | NGC |
| FOR 2562 | Mondeo II 2.0i | 97 | 20 | 96 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | NGD |
| FOR 1762 | Mondeo II 2.0i Turnier | 97 | 20 | 96 | 08/1996 - 09/2000 | NGA |
| FOR 945 | Orion II 1.4 | 86 | 14 | 54 | 02/1987 - 07/1990 | FUC |
| FOR 578 | Orion II 1.4 | 86 | 14 | 55 | 04/1986 - 07/1990 | FUA |
| FOR 964 | Orion II 1.4i | 86 | 14 | 54 | 10/1987 - 07/1990 | F6... |
| FOR 579 | Orion II 1.6 | 86 | 16 | 65 - 66 | 01/1986 - 07/1990 | LU... |
| FOR 581 | Orion II 1.6i | 86 | 16 | 66 | 04/1986 - 07/1990 | L4B |
| FOR 1261 | Orion II 1.6i | 86 | 16 | 75 | 08/1989 - 07/1990 | LJB |
| FOR 584 | Orion II 1.6i | 86 | 16 | 77 | 04/1986 - 07/1990 | LRB |
| FOR 1262 | Orion II 1.6i | 86 | 16 | 79 | 08/1989 - 07/1990 | LJA |
| FOR 1323 | Orion III 1.4 | 91 | 14 | 54 | 07/1990 - 12/1993 | FUH |
| FOR 1322 | Orion III 1.4i | 91 | 14 | 52 | 07/1990 - 12/1993 | F6F |
| FOR 1327 | Orion III 1.6i | 91 | 16 | 79 | 07/1990 - 09/1992 | LJE |
| FOR 1440 | Orion III 1.8i 16V | 91 | 18 | 77 | 02/1992 - 12/1993 | RDA |
| FOR 1874 | Puma 1.4i | 14 | 66 | 01/1998 - 11/2000 | FHD | |
| FOR 2553 | Puma 1.4i | 14 | 66 | 01/1998 - 11/2000 | FHF | |
| FOR 1784 | Puma 1.7i | 17 | 92 | 06/1997 - 12/2001 | MHA | |
| FOR 2554 | Puma 1.7i | 17 | 92 | 06/1997 - 12/2001 | MHB | |
| FOR 2910 | Ranger 2.3i | 23 | 100 | 06/1994 - 10/1997 | ||
| FOR 1883 | Ranger 2.5i | 25 | 89 | 11/1997 - 02/2001 | ||
| FOR 3367 | Sierra 1.6i | 87 | 16 | 59 | 10/1989 - 02/1993 | L6B |
| FOR 1235 | Sierra 1.6i | 87 | 16 | 59 | 10/1989 - 02/1993 | L6B |
| FOR 1236 | Sierra 1.6i Turnier | 87 | 16 | 59 | 10/1989 - 02/1993 | L6B |
| FOR 3386 | Sierra 1.8i | 87 | 18 | 63 | 04/1992 - 02/1993 | R6A |
| FOR 1881 | Sierra 1.8i | 87 | 18 | 63 | 04/1992 - 02/1993 | R6A |
| FOR 1882 | Sierra 1.8i Turnier | 87 | 18 | 63 | 04/1992 - 02/1993 | R6A |
| FOR 3121 | TE50 | AU | 50 | 200 | 10/1999 - 09/2000 | Z |
| FOR 3124 | TE50 | AU II | 50 | 220 | 10/2000 - 10/2001 | Z |
| FOR 3127 | TE50 | AU III | 56 | 250 | 11/2001 - 12/2002 | Z |
| FOR 3122 | TL50 | AU | 50 | 200 | 10/1999 - 09/2000 | Z |
| FOR 3125 | TL50 | AU II | 50 | 220 | 10/2000 - 10/2001 | Z |
| FOR 3128 | TL50 | AU III | 56 | 250 | 11/2001 - 12/2002 | Z |
| FOR 3123 | TS50 | AU | 50 | 220 | 10/1999 - 09/2000 | Z |
| FOR 3126 | TS50 | AU II | 50 | 220 | 10/2000 - 10/2001 | Z |
| FOR 3129 | TS50 | AU III | 56 | 250 | 11/2001 - 12/2002 | Z |
Learn everything about ignitions
Ignitions
Since electricity is not something we can physically see, the ignition system of our cars sometimes holds a little mystery or suspicion in its operation. It's important to realize that electricity, especially in an automotive setting, is not magic. And it's also important to realize that the ignition is key to your engine's performance. Your engine's overall performance is counting on that spark for complete combustion. Once you have a better understanding on how the ignition works and what each component actually does, things will begin to all make sense – and you'll be able to build the right ignition for your engine. Key goals of the ignition system:
- Produce and deliver a high-voltage spark from a low voltage supply source (the battery)
- This spark must be distributed to each combustion chamber as the piston nears top dead center on the compression stroke of the piston
- Control and even alter when the spark occurs in the cylinder to meet different engine demands
- Deliver a spark that has enough voltage and energy to ensure combustion of the fuel mixture
- Be able to reliably accomplish these goals throughout a variety of rpm, load, temperatures and conditions
Quick Overview
A typical (meaning stock) 12-volt automotive ignition system operates by taking in a low voltage with high current from the car's battery and changing it into a higher voltage with lower current to jump the spark plug gap to propagate combustion in the cylinder. This process of changing low voltage to high voltage, called induction, takes place in the coil. From there, the high voltage spark is transferred to the distributor and on to a spark plug wire which must deliver the spark to the cylinder that is coming up on the compression stroke.
Two Sides to Every Ignition
To help better understand the operation of the automotive ignition system, lets break the system into two sides: a primary side and a secondary side.
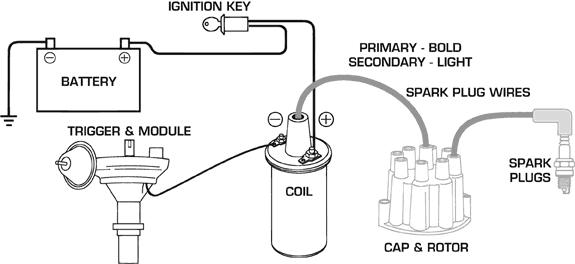
The Primary Side:
The best way to define the primary components is that they are the parts that deal with the low voltage from the battery (the 12-volt side). Note that all of these parts use conventional wiring, since they're carrying lower voltages (except the battery cables that connect to the starter and alternator). This includes the battery itself, the ignition switch, a switching device and the wiring that connects to the coil's negative and positive terminals. The coil works both sides of the fence since it is the point where the primary and secondary systems meet as it takes a high voltage in but sends out a high voltage spark.
The Secondary Side:
The spark plug wire that connects the coil to the center terminal of the distributor (called the coil wire) is where the secondary side of the ignition begins. In stock systems, there is generally anywhere from 10,000 – 20,000 volts bolting through this wire. This spark zips through the wire and transfers to the rotor tip and then jumps across a small gap to another cap terminal. From there it moves out of the cap, through a spark plug wire, and finally across the spark plug gap. It is important to note that these secondary components, the cap, rotor and wires, are maintenance parts. Depending on your use, they should be inspected at least once every cruise season and numerous times during a race system.
Ignition Maintenance
Even though we're dealing with electronics, it's important to inspect your ignition system. Remember that the ignition system, at least the high voltage side, requires maintenance. Over time, the rotor tip wears as does the carbon contact of the distributor cap. Spark plug wires also grow weary over time from delivering voltages that can range from 10,000 to 40,000 volts. Plus, your wires operate in a harsh, nasty environment with extreme heat cycles, moving parts, oils and fluids all working against them.
- It is recommended to inspect the cap and rotor at least once a year. If you live in an area with high humidity, you may want to inspect it more often.
- Visually inspect the cap and rotor for wear of the cap terminals and the rotor tip.
- Look for traces of carbon tracks where spark scatter occurs.
- Visually inspect the plug wires for burns or tears. Also, it is a good idea to periodically check the resistance of the wires so see if there is a wire with excessive resistance indicating a break in the conductor.
The Coil
If there is a single part of the ignition that can holds some mystery to its operation, it is the coil. In a stock ignition system, 12 – 14 volts are delivered to the coil via the positive and negative terminals. Within the wink of an eye, it sends and output of 15,000 volts or higher! But there is no slight-of-hand taking place here – it's all a carefully crafted lesson in electronics. And one that can be tuned to meet a variety of output requirements.
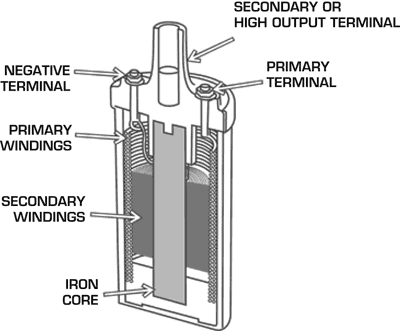
A coil consists of two sets of windings made up of insulated wires that surround an iron or similar metal core. The primary windings are generally made up of several hundred turns of a heavy wire while the secondary set consists of a much smaller gauge wiring that makes up thousands of turns. Coil manufacturers use a ratio between the secondary and primary winding numbers as a specification such as 100:1, which would mean 100 secondary turns to every one of the primary. This is a commonly used specification you will see in the coil information given by many manufacturers.
In a typical factory-style inductive ignition, current from the battery flows through the thicker primary windings when the switching device (points or magnetic pickups) is closed. This creates a magnetic field that builds strength thanks to the help of the iron core.
When the switching device opens (the trigger signal) the flow of current is broken and this magnetic field collapses over to the thousands of secondary windings. During this collapse, the voltage is stepped up, creating the higher voltage that is required to jump the spark plug gap and ignite the air/fuel mixture. This process is called inductance.
When shopping for a coil, keep in mind that the windings, materials and resistances of the coils can be altered to design coils for the street or for racing ignitions. Also there are a variety of sizes and shapes available today. Most manufacturers will explain what application the coils are used for so you should have no trouble finding a coil for your application.
Distributor Operation
The distributor of a typical engine has a lot more responsibility than just distributing the spark to the correct cylinder (which in itself is a feat). It is also triggers the coil to release the high voltage, in many cases it turns the oil pump, it distributes the spark to eight different cylinders and it alters the timing of the system. The distributor could be the hardest working part of your ignition system and this is why it is important to ensure that your distributor is up to the task of delivering the performance and power that you expect from your engine.
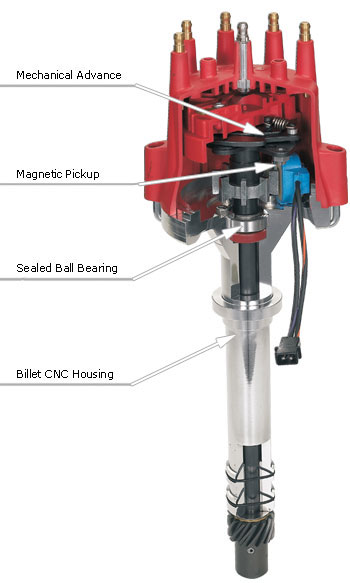
Distributors have changed over the years. From plastic to billet housing materials, trigger mechanisms, timing controls and other items have all been modified over the years, yet most models will perform some if not all of the following duties:
- Distribute the spark to different cylinders
- Trigger the secondary side of the ignition
- Alter the ignition timing
- Driving the oil pump
Most distributors are driven by the camshaft through gears with a one-to-one ratio. (This means the distributor turns at camshaft speed, or half of crank speed.) There are a two important parts attached to the shaft; a trigger wheel and the rotor. The trigger wheel will vary depending on the type of trigger being used, but you will notice that it will have a tooth, or lobe or space for each cylinder of the engine. The rotor delivers the high voltage from the coil to the correct cap terminal. When the coil fires, the voltage is transferred through the coil wire to the center terminal of the distributor cap. This terminal contacts the center of the rotor, moves across the rotor and jumps across a small gap to the spark plug terminal of the cap. All of this occurs in fractions of a second and thousands of times.
Common Firing Orders for Domestic Vehicles
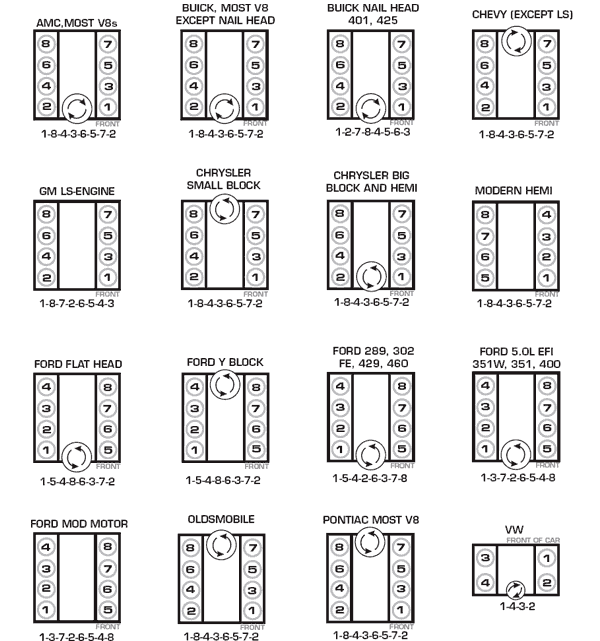
Spark Plugs
The spark plug is the final step for the ignition process. All of the voltage and energy build up to make a final leap across the plug gap which initiates combustion of the fuel mixture.
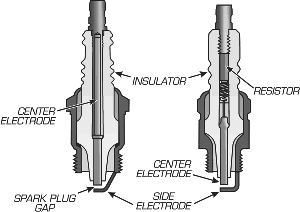
The spark travels through the plug wire terminal to the threaded tip of the plug's center terminal. This terminal reaches all the way through the ceramic shell of the plug and ends at the electrode. The electrode is centered in the plug with a gap between it and the tip of which is connected to the metal housing of the plug forming a ground to the engine. The voltage jumps this gap to reach ground, resulting in a spark that ignites the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder.
One physical adjustment you can make with most plugs is the distance of the spark plug gap. Opening the gap forces the coil to build up a higher voltage in order for the spark to jump the gap.
Too large of a gap will also put added pressure on the secondary side of the ignition system, resulting in shortening the life of the components. Too small of a gap can make life too easy on the ignition to the point where the resulting in a weak spark that may not be strong enough to create a full combustion cycle of the air/fuel mixture.
There are a variety of spark plugs available from simple to exotic designs. And of course each one has their own theories on why one is better than the other. There are platinum-tipped plugs, plugs with tiny electrodes, some with numerous electrodes, and more. There are also spark plugs called resistor plugs, non-resistor plugs, hot plugs, and cold plugs. It is best to follow your engine builder's recommendation for plugs, or to test and tune with gaps and different brands.
Spark Plug Wires
The spark plug wires are the arteries of the ignition system. They provide the all-important path that allows the spark to transfer from the distributor cap to the spark plugs. The importance of good quality spark plug wires cannot be stressed enough! Plug wires live in a nasty environment and deal with high heat, abrasion, and getting whipped around at high speeds. They also need to be able to deliver high levels of voltage, while suppressing electromagnetic interference (EMI), which is created when high voltage passes through a wire.
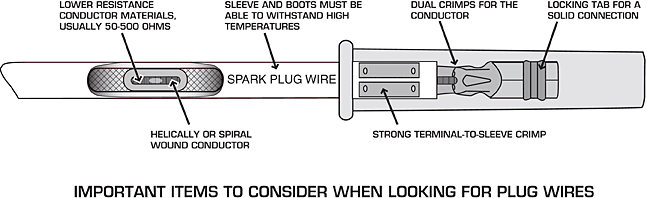
EMI refers to electrical noise or interference. Not only can it be an annoying buzz through the radio, but it can also wreak havoc on other electronics such as the rev limiter, or even the ECU of a car equipped with an EFI system. Original equipment spark plug wires combat EMI by using a carbon core material that has a very high resistance to the flow of the spark energy. The aftermarket offers a variety of wire sets that offer much lower resistance to ensure the most spark possible reaches the plugs.
When you're shopping for wires, look for lower resistance (measured in ohms), but also look for good EMI suppression. Another area of importance in the spark plug wire is the crimp between the terminal and the wire. Poor crimps can contribute to intermittent performance, a dead cylinder, and other problems. Also pay attention to the spark plug wire boots, as they need to survive parked in close proximity to the exhaust manifolds where heat is at its most extreme.
Battery and Charging System
You can have the most powerful ignition available and tuned to perfection, but without a battery to fire things up, you'll be going no where. The battery is the main source of power for a performance ignition system, and you need to be sure that it's capable of having the juice you need get the engine fired up. Not to mention to supply the ignition with current and voltage created by the alternator.
There's more relying on the battery than just the ignition system. The starter is also pulling huge amounts of current to crank over your engine. Adding compression and big strokes adds to this demand as well. Also, any other electrical devices such as fans, pumps, motors, and even fuel injection controls all tap into the battery for voltage.
When looking for a batter, certainly look at the cold cranking amps (CCA) racing. Also look at the cycling, or recovery capabilities of the battery.
Alternators are used on all street cars and even on the majority of race engines (except purpose built drag cars for the most part). The alternator is responsible for producing the electricity that a car draws from the battery while it is running. The alternator generates an alternating current (AC) when it is turned by a belt and pulley system connected to the crankshaft. Inside the alternator, a rotor spins to create a magnetic field. This field is induced into the windings of a stator (around the rotor), and eventually makes its way to the battery as direct current (DC).
If you run a battery without a charging system, it is important that it's fully charged at the beginning of the race so it has the capacity to power all of your car's electrical needs through the finish line.
Capacitive Discharge Ignitions
The biggest downfall of the inductive ignition design is the storage and build-up of the voltage. It takes a certain amount of time, called dwell or coil saturation, for the coil to transform the lower battery voltage to the higher voltage required to jump the spark plug gap. This system works well for OEM and general use, but falls short when it comes to increased performance and high rpm. This can result in a low voltage spark output that may not be powerful enough to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. This can result in a misfire and loss of power.
Capacitive discharge (CD) ignition controls are the most common upgrade when it comes to improving the output of the ignition. The biggest advantage is that they are able to produce higher voltages from idle to red-line rpm. This is because a CD ignition draws its voltage supply directly from the battery and incorporates a transformer that steps this voltage up to close to 500 volts in many systems. A capacitor in the ignition stores this high voltage and fires it all when the distributor triggers it.
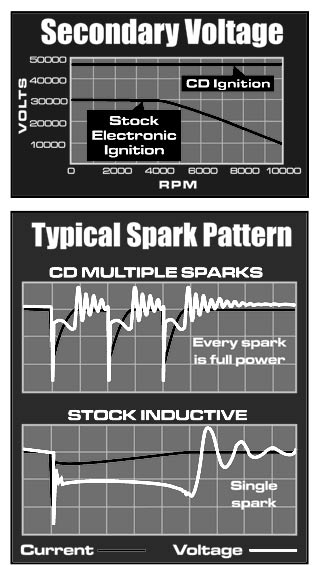
The one short coming of a CD ignition is that the spark has very short duration. This isn't a problem at higher rpm, but could be a lower rpm. However, engineers found that with the increased voltage and nearly instant recovery, the spark can be fired multiple times on the same cycle, hence multiple spark ignitions (or multi-strike, or second strike, etc…). At an idle there may be five or six sparks, and as rpm increases, the number of sparks decreases. Generally, most CD ignitions produce multiple sparks through about 3,000 rpm. Keep in mind that we're discussing cycles that occur within milli-seconds!
A lot of people look at CD ignitions as race-only pieces, but that is not the case. In fact, a lot of these ignitions are legal to install on pollution-controlled engines – and some are even legal to install on OBD-II equipped cars. Most ignition controls are nearly universal in their application, as they can be installed on most anything with a distributor. Of course, distributors haven't been used on newer vehicles for several years, but there are also ignitions and coils available for these distributorless systems as well. These will be discussed in later chapters as well.
The series of full-power sparks that most CD ignitions produce creates more heat in the cylinder, resulting in improved combustion of the air/fuel mixture. In most cases, the benefits include an improved idle, quick starts, crisp throttle response, and improved high-RPM performance. If you have an engine that burns a little oil, runs a touch on the rich side, or the like, a multiple sparking ignition, CD or inductive, could help overcome these performance issues. That is, until they can be remedied correctly.